Overview¶
Jupyter: friendly R and Python experience¶
Jupyter gives you notebooks to write your code and make visualizations. You can quickly iterate, visualize, and share your analyses. Because it's running on a server (that you set up in the Kubeflow section) you can do really big analyses on centralized hardware, adding as much horsepower as you need! And because it's on the cloud, you can share it with your colleagues too.
Explore your data¶
Jupyter comes with a number of features (and we can add more)
- Integrated visuals within your notebook
- Data volume for storing your data
- You can share your workspace with colleagues.
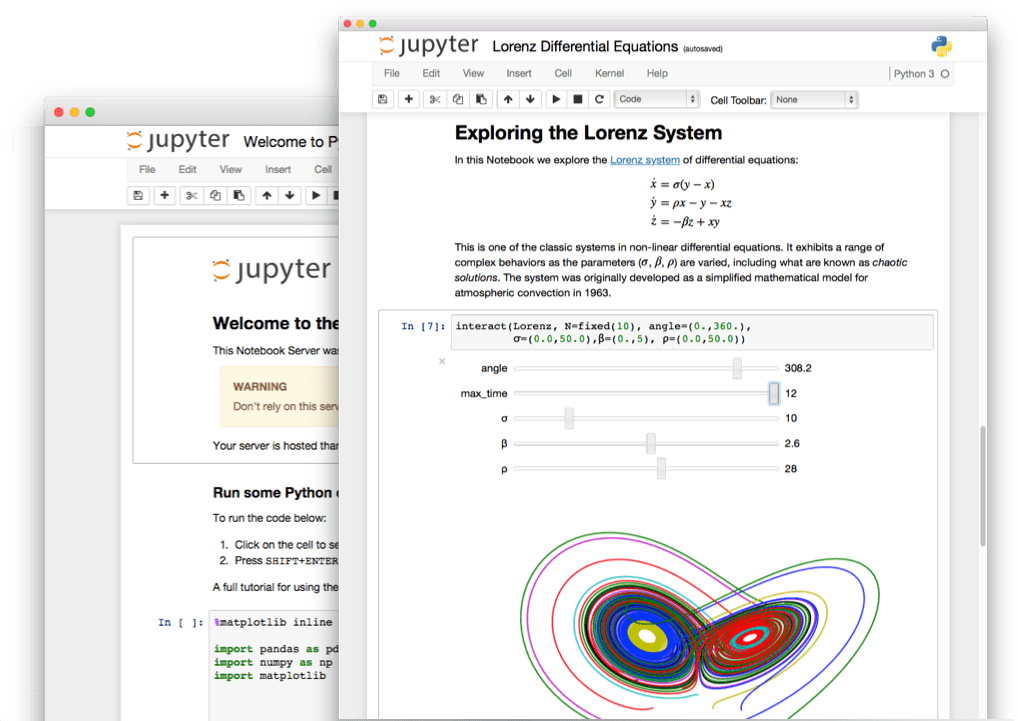
Explore Your Data with an API¶

Use Datasette , an instant JSON API for your SQLite databases. Run SQL queries in a more interactive way!
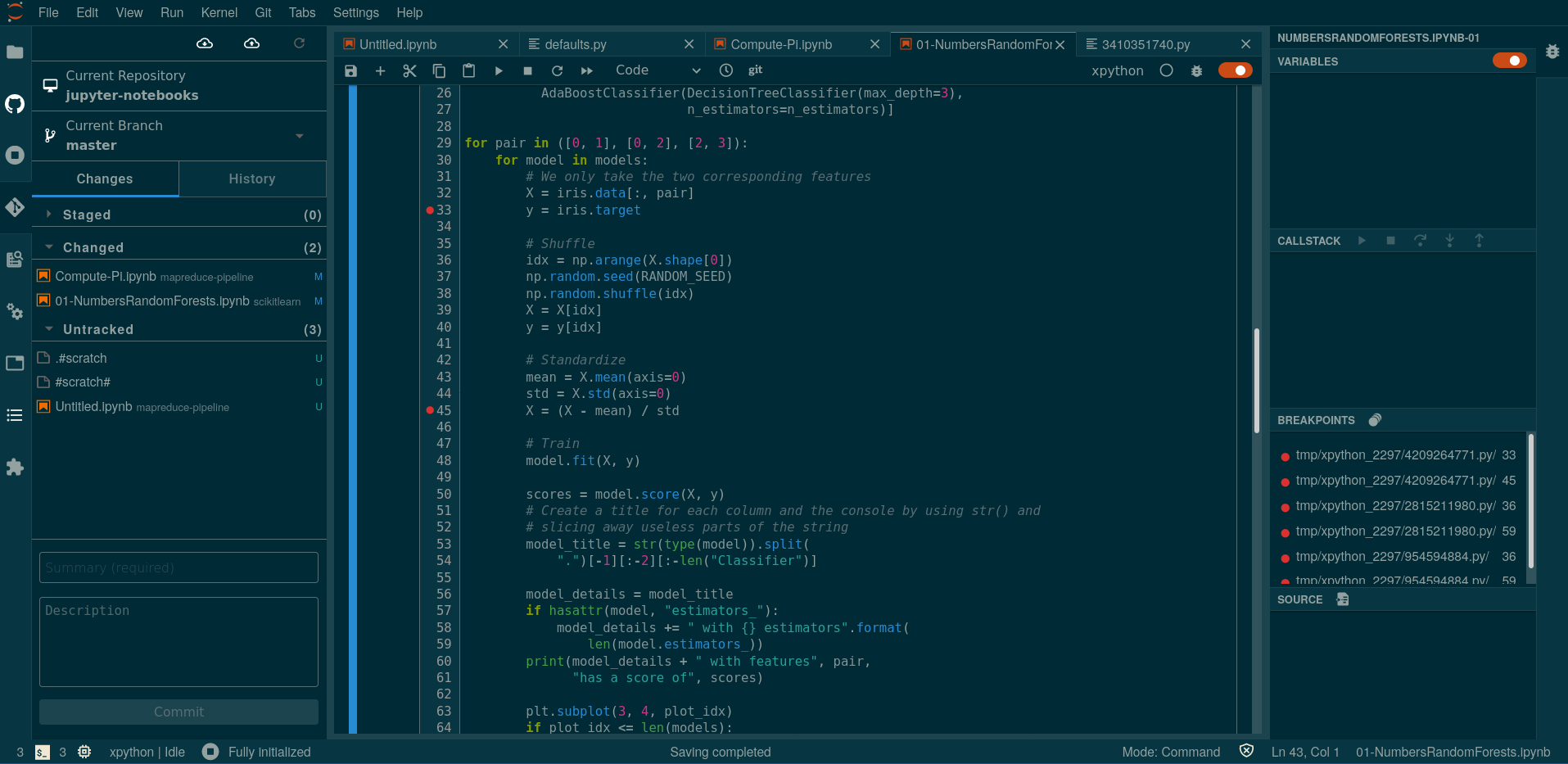
IDE in the browser¶
Create for exploring, and also great for writing code
- Linting and a debugger
- Git integration
- Built in Terminal
- Light/Dark theme (change settings at the top)
More information on Jupyter here
Setup¶
Get started with the examples¶
When you started your server, it got loaded with a bunch of example notebooks. Double click to open the jupyter-notebooks folder. Great notebooks to start with are R/01-R-Notebook-Demo.ipynb, or the notebooks in scikitlearn. pytorch and tensorflow are great if you are familiar with machine learning. The mapreduce-pipeline and ai-pipeline are more advanced.
Some notebooks only work in certain server versions
For instance, gdal is only in the geomatics image. So if you use another image then a notebook using gdal might not work.
Adding software¶
You do not have sudo in Jupyter, but you can use
or
Don't forget to restart your Jupyter kernel afterwards, to make new packages available.
Make sure to restart the Jupyter kernel after installing new software
If you install software in a terminal, but your Jupyter kernel was already running, then it will not be updated.
Is there something that you can't install?
If you need something installed, reach us or open a GitHub issue. We can add it to the default software.
Once you've got the basics ...¶
Getting Data in and out of Jupyter¶
You can upload and download data to/from JupyterHub directly in the menu. There is an upload button at the top, and you can right-click most files or folders to download them.
Shareable "Bucket" storage¶
There is also a mounted buckets folder in your home directory, which holds files in Azure Blob Storage.
Refer to the Storage section for details.
Data Analysis¶
Data analysis is an underappreciated art.
Data analysis is the process of examining and interpreting large amounts of data to extract useful insights and draw meaningful conclusions. This can be done using various techniques and tools, such as statistical analysis, machine learning, and visualization. The goal of data analysis is to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships in the data, which can then be used to inform decisions and solve problems. Data analysis is used in a wide range of fields, from business and finance to healthcare and science, to help organizations make more informed decisions based on evidence and data-driven insights.
JupyterLab¶
Process data using R, Python, or Julia in JupyterLab

Processing data using R, Python, or Julia is made easy with the Advanced Analytics Workspace. Whether you're new to data analysis or an experienced data scientist, our platform supports a range of programming languages to fit your needs. You can install and run packages for R or Python to perform data processing tasks such as data cleaning, transformation, and modeling. If you prefer Julia, our platform also offers support for this programming language.